China’s Transformation: From Low-Cost Factory to High-Tech Leader
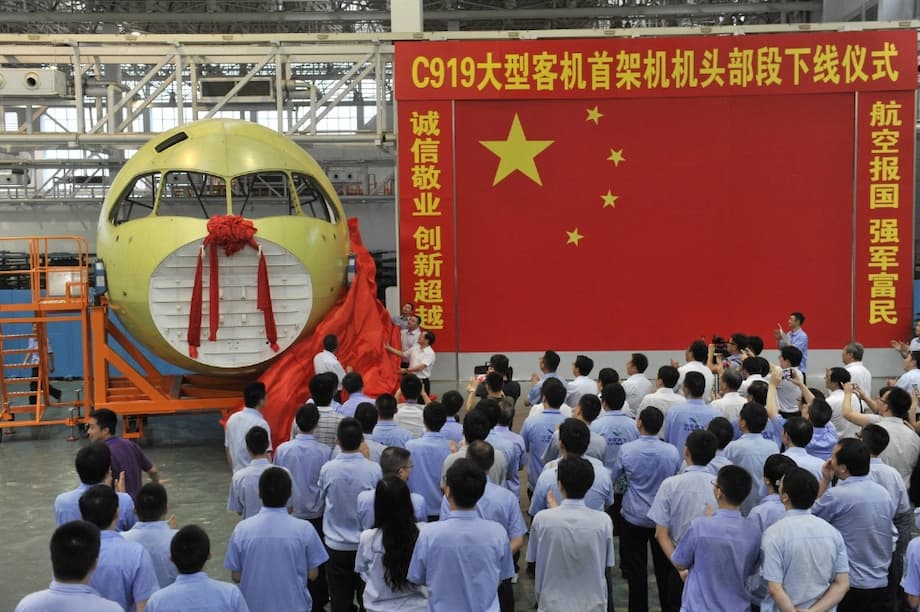
For decades, China was known as the world’s low-cost manufacturing hub, churning out everything from toys to textiles for global brands. Today, that image is outdated. China has rapidly evolved into a powerhouse of high-tech manufacturing, rivaling and even surpassing established leaders in sectors like electric vehicles, robotics, clean energy, and advanced electronics. This transformation is not only reshaping global supply chains but also challenging the technological dominance of the West.
- China’s Transformation: From Low-Cost Factory to High-Tech Leader
- How Did China Achieve High-Tech Manufacturing Dominance?
- Innovation at Scale: China’s Breakthroughs in Key Sectors
- Challenges and Limitations: Can China Sustain Its Momentum?
- Global Impact: How China’s Rise Is Reshaping the World
- In Summary
What makes China’s rise especially remarkable is that it has achieved technological leadership in many sectors despite a per capita GDP that remains far below that of the United States and other developed economies. The country’s manufacturing output now dwarfs that of its closest competitors, and its influence is felt in nearly every corner of the global economy.
How Did China Achieve High-Tech Manufacturing Dominance?
China’s ascent in high-tech manufacturing is the result of a complex interplay of factors: strategic government policy, massive investments in education and infrastructure, a vast domestic market, and an ecosystem that encourages both competition and collaboration. Understanding these drivers is key to grasping the scale and significance of China’s industrial revolution.
The Power of Scale and Human Capital
One of China’s greatest advantages is its sheer size. With a population of over 1.4 billion, China has been able to cultivate an enormous pool of skilled workers and engineers. Early on, the government prioritized education, especially in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Over the past four decades, university enrollment has soared, producing millions of graduates each year—far more than any other country. Many of these graduates have studied abroad, bringing back valuable expertise and global perspectives.
This investment in human capital has enabled Chinese companies to quickly absorb and improve upon foreign technologies, develop their own innovations, and provide high-quality, affordable after-sales services. The result is a workforce that not only builds products but also drives process improvements and technological breakthroughs.
Strategic Industrial Policy: Made in China 2025 and Beyond
China’s government has played a central role in guiding the country’s industrial transformation. The Made in China 2025 initiative, launched in 2015, set ambitious targets for leadership in ten strategic sectors, including advanced robotics, aerospace, clean energy, and next-generation information technology. The plan provided generous subsidies, tax incentives, and support for research and development, while also encouraging foreign firms to localize production and transfer technology.
Despite international criticism and U.S. tariffs aimed at curbing China’s ambitions, the core objectives of Made in China 2025 have continued under different names and frameworks. The results are visible: China now leads in electric vehicles, batteries, solar panels, and industrial robotics, and is rapidly closing the gap in areas like semiconductors and biotechnology.
Building a World-Class Industrial Ecosystem
China’s manufacturing success is not just about government planning. The country has developed a dense network of suppliers, innovators, and logistics providers, creating an ecosystem where ideas and products can move quickly from concept to market. Cities like Shenzhen have become global centers for hardware innovation, attracting entrepreneurs and engineers from around the world.
Competition among local governments has also spurred industrial development. Provinces and cities vie to attract investment, build infrastructure, and foster clusters of high-tech firms. This “horizontal competition” has led to rapid scaling and constant upgrading of manufacturing capabilities.
Innovation at Scale: China’s Breakthroughs in Key Sectors
China’s high-tech ambitions are most visible in sectors where it has achieved global leadership or is rapidly catching up. The country’s approach combines massive investment, process innovation, and relentless scaling—often driving down costs and making advanced technologies accessible worldwide.
Electric Vehicles and Batteries: Driving the Future
China is now the world’s largest producer and consumer of electric vehicles (EVs). Companies like BYD and CATL have not only surpassed global competitors in sales but also in technological innovation. BYD overtook Tesla in 2024 as the world’s top EV maker, while CATL leads in battery production, thanks to breakthroughs in lithium iron phosphate technology that make batteries lighter, safer, and cheaper.
China’s dominance in EVs and batteries is underpinned by a robust supply chain, government incentives, and a vast domestic market that allows for rapid scaling and experimentation. The country has also become a leader in clean energy patents, with Chinese firms filing more high-quality patents in batteries and solar technology than any other nation.
Robotics and Automation: The Next Frontier
China is investing heavily in robotics and automation to maintain its manufacturing edge. Over the past decade, its share of global industrial robot installations has soared from about one-fifth to more than half. Domestic robot manufacturers have rapidly increased their market share, especially in industries like electronics and machinery, where automation is critical for efficiency and quality.
In 2025, China’s National Development and Reform Commission announced a state-backed venture capital fund worth nearly 1 trillion yuan (US$138 billion) to support robotics, artificial intelligence, and other cutting-edge technologies. The country’s latest five-year plan positions humanoid robots as a frontier technology, aiming to integrate robotics with AI and smart manufacturing applications.
Clean Energy: From Copycat to Innovator
Once accused of copying Western clean energy technologies, China now leads in solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries. The scale of Chinese investment has allowed it to build entire industries from scratch, dominating global supply chains and driving down the cost of renewable energy worldwide. In 2022, Chinese companies filed more than 5,000 internationally competitive clean energy patents, compared to just 18 in 2000.
China’s approach to innovation is both strategic and ruthless. The government floods emerging sectors with subsidies, encourages fierce competition, and then withdraws support, allowing only the strongest companies to survive and expand globally. This “economic Darwinism” has produced world leaders like BYD and CATL, whose patented technologies are setting new standards in safety and performance.
Biotechnology: Cheaper, Faster, and Growing
China’s biotech industry is another area of rapid growth. The country has focused on making drug development and manufacturing faster and more affordable, attracting global pharmaceutical companies to its hubs. Firms like Wuxi AppTec offer end-to-end services for drug research and production, leveraging China’s large pool of medical graduates and streamlined regulatory processes.
While China still lags behind the U.S. in breakthrough scientific research, its efficiency and cost advantages are reshaping the global biotech landscape. The country is also making strides in innovative treatments, such as mRNA cancer vaccines, offered at a fraction of Western prices.
Challenges and Limitations: Can China Sustain Its Momentum?
Despite its impressive achievements, China’s high-tech manufacturing juggernaut faces significant challenges. The country remains dependent on foreign technology in critical areas like advanced semiconductors and high-end manufacturing equipment. U.S.-led restrictions on technology transfers and ongoing trade tensions have made it harder for Chinese firms to access the latest chips and tools.
There are also concerns about inefficiencies and overcapacity, as local governments sometimes invest in duplicative projects. In some sectors, rapid expansion has led to waste and slowed economic growth. Quality and safety issues persist, especially in pharmaceuticals and medical devices, though Chinese firms are increasingly meeting global standards.
Moreover, as China’s economy matures, it must shift from imitation and process innovation to original research and scientific breakthroughs. The government is investing heavily in basic research and scientific training, but catching up to the West in frontier science will take time.
Global Impact: How China’s Rise Is Reshaping the World
China’s dominance in high-tech manufacturing has profound implications for the global economy. The country’s vast manufacturing base gives it a competitive edge in most sectors, and global supply chains are deeply intertwined with Chinese production. Decoupling from China is seen as difficult and disruptive, especially for industries like electronics, clean energy, and automotive manufacturing.
Foreign multinationals continue to invest in China, attracted by its advanced infrastructure, efficient supply chains, and growing consumer market. Companies like Germany’s Chiron Machine Tools and Italy’s Conti Valerio have expanded their operations in China, leveraging local talent and innovation to boost exports and productivity.
At the same time, China’s rise has triggered a strategic response from the United States and its allies. Policymakers are debating how to compete with China’s model of “national power capitalism,” which combines state support, strategic investment, and techno-economic strength. Some experts argue that the West must invest more in industrial research, workforce training, and supply chain resilience to maintain its competitive edge.
Reverse Dependencies and the New Global Order
China’s success has also created “reverse dependencies,” where the world increasingly relies on Chinese production for critical goods. In sectors like batteries, solar panels, and electric vehicles, China’s dominance means that global innovation and the energy transition are heavily dependent on Chinese technologies. The country has even begun restricting the export of certain manufacturing technologies to protect its lead.
This new reality is forcing governments and companies worldwide to rethink their strategies. While some see China’s rise as a threat, others view it as an opportunity to lower costs, accelerate innovation, and address global challenges like climate change.
In Summary
- China has transformed from a low-cost manufacturing base to a global leader in high-tech industries such as electric vehicles, robotics, and clean energy.
- Key drivers of this success include massive investments in education, strategic government policies like Made in China 2025, and a vast, competitive industrial ecosystem.
- China leads the world in manufacturing output, patent filings, and process innovation, driving down costs and making advanced technologies widely accessible.
- Challenges remain in achieving self-sufficiency in critical technologies like semiconductors, and the country faces inefficiencies and quality concerns in some sectors.
- China’s rise is reshaping global supply chains, creating new dependencies, and prompting strategic responses from the United States and other countries.
- The future of global innovation and economic power will depend on how China and the rest of the world adapt to this new era of high-tech competition.